Work Energy Theorem
Work Energy Theorem: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Kinetic Energy and Work Energy Theorem.
Important Questions on Work Energy Theorem
A satellite of mass , initially at rest on the earth, is launched into a circular orbit at a height equal to the radius of the earth. The minimum energy required is
of work is done in sliding a block slowly up an inclined plane of height . Taking . Work done against friction is:
A ball whose kinetic energy is , is projected at an angle of with the horizontal. The kinetic energy of the ball at the highest point of its flight will be,
A ball whose kinetic energy is E, is projected at an angle of to the horizontal. The kinetic energy of the ball at the highest point of its flight will be –
If the momentum of the body increases by then the increase in Kinetic energy of the body is
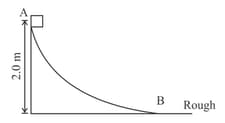
The block weighing starts slipping on the track from a point above the horizontal surface. It travels down a smooth, fixed and curved track joined to a rough horizontal surface (see figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of with the block. The distance it moves on the rough surface is,
When mass and speed are doubled the increases
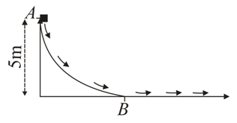
An object of mass is sliding under gravity from point to point on a frictionless slide from a height of , as shown in the figure. After what distance will the object stop on the following flat track beyond point . if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the flat track and the object is
A particle of mass is thrown vertically upward with a speed of . The work done by the force of gravity during the time the particle goes up is
The acquired by a mass in travelling a certain distance , starting from rest, under the action of a constant force is directly proportional to:
A block moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of compresses an ideal spring and comes to rest, if the force constant of the spring be , then the spring is compressed by
Two masses of and are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitude of their momenta is
Kinetic energy of a body can be increased more by _____.
A shell explodes in mid-air. It's total:
The displacement of particle of mass moving along straight line is given as The work done by the force in first is
An air molecule of mass and moving with a speed of has a kinetic energy of about
A body of mass thrown vertically upward from the ground with a velocity of reaches a maximum height of . Magnitude of work done by the air resistance is (Acceleration due to gravity )
A car of mass is moving at a speed of up an inclined plane making an angle with the horizontal. At some point, the motor stops, and the car continues to move along the plane due to its initial velocity. If it is just able to reach the destination which is at a height of above the point, calculate the work done against friction acting between the tyres of the car and the plane. (Assume )
If the linear momentum is increased by then the kinetic energy will increase by
An object of mass moves along positive axis. When it passes through a constant force directed along the negative axis begins to act on it. The kinetic energy of the object is found to be and for and respectively. If the force continues to act further, then the object moves back along negative axis. The speed of the object when it reaches
